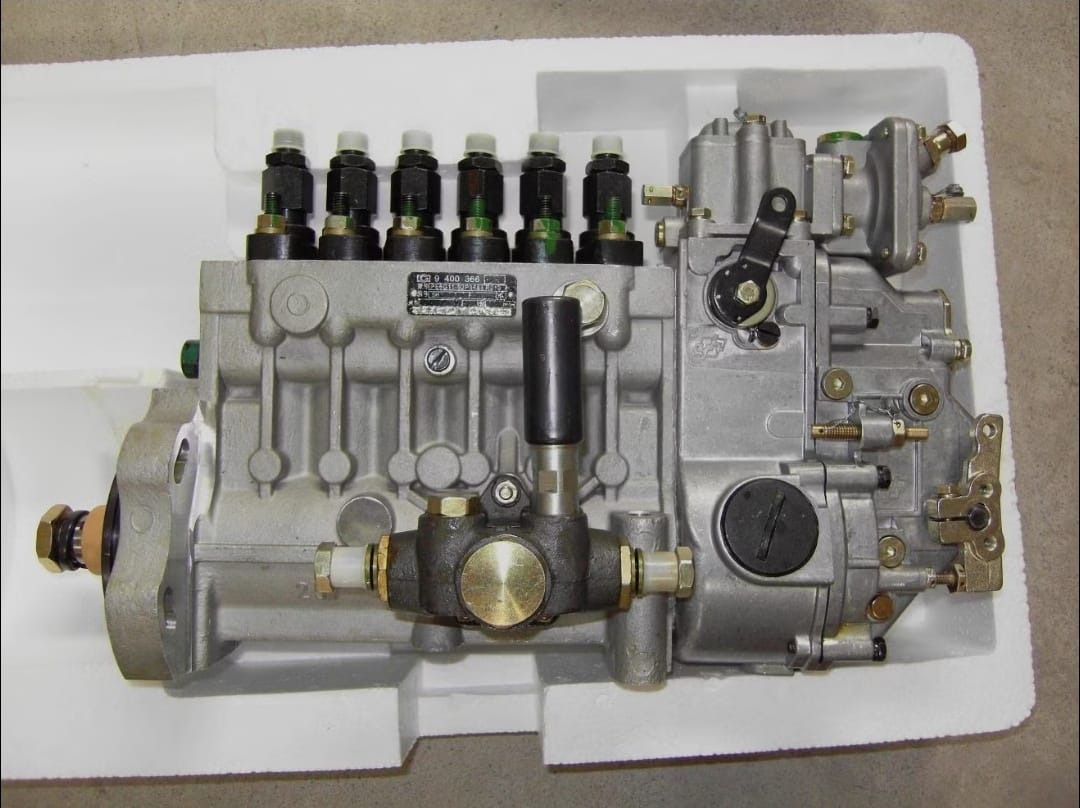
Components of the Inline Diesel Fuel Injection Pump
The inline fuel injection pump is one of the most important components of the diesel engine’s fuel injection system. It controls the quantity, pressure, and timing of diesel injection into the combustion chambers to ensure efficient engine operation. The pump consists of several key parts, each performing a specific function to achieve optimal combustion.
1- Camshaft
It is the shaft responsible for operating the pump plungers. The camshaft rotates with the engine, and its lobes push the plungers at the correct timing and motion, helping control fuel quantity and pressure.
2- Plungers
There are plungers equal to the number of engine cylinders. They move up and down to pressurize the fuel inside the pumping chamber. As the plunger moves upward, the pressure increases and the diesel is delivered toward the injector.
3- Barrel or Pumping Element
This is the chamber in which the plunger moves. It is responsible for maintaining the high pressure generated by the plunger before sending the fuel to the injector.
4- Delivery Valve
Located at the top of the pumping chamber. Its function is to regulate the fuel leaving the pump toward the injection lines and to prevent pressure from returning to the plunger after the injection process is completed.
5- Governor
A vital component that controls the amount of fuel supplied according to engine speed. It prevents over speeding and ensures stable engine operation under different loads.
6- Drive Gear
Connects the pump to the crankshaft or timing system. It transfers rotational motion from the engine’s crankshaft to the injection pump.
7- Feed Pump
A small auxiliary pump attached to the main injection pump. It draws diesel from the tank and supplies it at low pressure into the main injection pump.
8- Tappet (or Cam Follower)
It transfers motion from the camshaft to the plunger. As the pump cam rotates, it pushes the tappet, which then pushes the plunger upward from the suction position to the compression position.
9- Internal Fuel Screen
A small internal mesh filter that traps fine debris before the fuel enters the pump's internal passages.
10- Pump Housing
The outer body that contains and supports all internal pump components and maintains structural stability.
11- Plunger Spring
Its function is to return the plunger to the suction position after the cam pushes it downward.